Glucosamine Sulfate For Knee and Spinal Arthritis
(Taken from Medline Plus a service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine and National Institute of Health)
Glucosamine sulfate is commonly used for arthritis. Scientists have studied it extensively for this use. It is most often used for a type of arthritis called osteoarthritis. This is the most common type of arthritis.
Over the years, people have tried glucosamine sulfate for a variety of other uses. For example, it has been tried for glaucoma and for weight loss. But glucosamine sulfate has not been adequately studied for these uses. There is no proof that glucosamine sulfate is beneficial for these conditions.
There are different forms of glucosamine including glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride, and N-acetyl-glucosamine. These different chemicals have some similarities; however, they may not have the same effects when taken as a dietary supplement. Most of the scientific research done on glucosamine has been done on glucosamine sulfate. The information on this page pertains to glucosamine sulfate. For information on the other forms of glucosamine, see the specific pages for each of them.
Dietary supplements that contain glucosamine often contain additional ingredients. These additional ingredients are frequently chondroitin sulfate, MSM, or shark cartilage. Some people think these combinations work better than taking just glucosamine sulfate alone. So far, researchers have found no proof that combining the additional ingredients with glucosamine adds any benefit.
Glucosamine is also in some skin creams used to control arthritis pain. These creams usually contain camphor and other ingredients in addition to glucosamine. Researchers believe that any pain relief people may experience from these creams is due to ingredients other than glucosamine. There is no evidence that glucosamine can be absorbed through the skin.
Some glucosamine sulfate products are not labeled accurately. In some cases, the amount of glucosamine actually in the product has varied from none to over 100% of the amount stated on the product’s label. Some products have contained glucosamine hydrochloride when glucosamine sulfate was listed on the label.
How effective is it?
The effectiveness ratings for GLUCOSAMINE SULFATE are as follows:
Likely effective for...
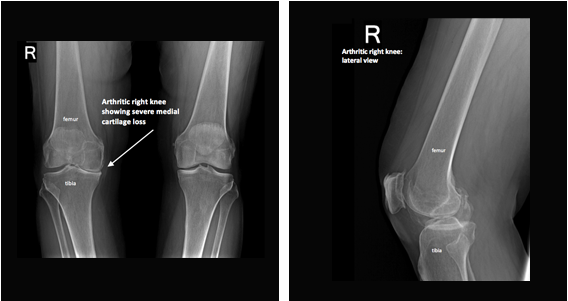
- Osteoarthritis. Most research on glucosamine sulfate has measured its effectiveness on osteoarthritis of the knee. However, there is some evidence that it might also help osteoarthritis of the hip or spine.
Some research suggests that glucosamine reduces pain of osteoarthritis in the knee about as well as the over-the-counter pain reliever acetaminophen (Tylenol). It also seems to reduce pain about as much as the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and piroxicam (Feldene). However, there is a difference between glucosamine sulfate and these drugs in the time it takes to reduce pain. The NSAIDs, such as Motrin, Advil, and Feldene, relieve symptoms and reduce pain usually within about 2 weeks, but glucosamine sulfate takes about 4-8 weeks.
Glucosamine sulfate does not seem to decrease pain in everyone who takes it. Some people get no benefit. Some research shows that glucosamine sulfate might not work very well for people with more severe, long-standing osteoarthritis, or for people who are older or heavier.
In addition to relieving pain, glucosamine sulfate might also slow the breakdown of joints in people with osteoarthritis who take it long-term. Some researchers hope that glucosamine sulfate might keep osteoarthritis from getting worse as quickly as it otherwise might. There is some evidence that people who take glucosamine sulfate might be less likely to need total knee replacement surgery.
How does it work?
Joints are cushioned by the fluid and cartilage that surround them. In some people with osteoarthritis, the cartilage breaks down and becomes thin. This results in more joint friction, pain, and stiffness. Researchers think that taking glucosamine supplements may either increase the cartilage and fluid surrounding joints or help prevent breakdown of these substances, or maybe both.
Some researchers think the “sulfate” part of glucosamine sulfate is also important. Sulfate is needed by the body to produce cartilage. This is one reason why researchers believe that glucosamine sulfate might work better than other forms of glucosamine such as glucosamine hydrochloride or N-acetyl glucosamine. These other forms do not contain sulfate.
Are there safety concerns?
Asthma: There is one report linking an asthma attack with taking glucosamine. It is not known for sure if glucosamine was the cause of the asthma attack. Until more is known, people with asthma should be cautious about taking products that contain glucosamine.
Diabetes: Some early research suggested that glucosamine sulfate might raise blood sugar in people with diabetes. However, more recent and more reliable research now shows that glucosamine sulfate does not seem to affect blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes. Glucosamine appears to be safe for most people with diabetes, but blood sugar should be monitored closely.
High cholesterol: Animal research suggests that glucosamine may increase cholesterol levels. In contrast, glucosamine does not seem to increase cholesterol levels in humans. However, some early research suggests that glucosamine might increase insulin levels. This might cause cholesterol levels to increase. To be cautious, if you take glucosamine sulfate and have high cholesterol, monitor your cholesterol levels closely.
High blood pressure: Early research suggests that glucosamine sulfate can increase insulin levels. This might cause blood pressure to increase. However, more reliable research suggests that glucosamine sulfate does not increase blood pressure. To be cautious, if you take glucosamine sulfate and have high blood pressure, monitor your blood pressure closely.
Shellfish allergy: Because some glucosamine sulfate products are made from the shells of shrimp, lobsters or crabs, there is concern that glucosamine products might cause allergic reactions in people who are allergic to shellfish. However, allergic reactions in people with shellfish allergy are typically caused by the meat of shellfish, not the shell. There are no reports of allergic reactions to glucosamine in people who are allergic to shellfish. There is also some information that people with shellfish allergy can safely take glucosamine products.
Surgery: Glucosamine sulfate might affect blood sugar levels and might interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgery. Stop taking glucosamine sulfate at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Are there interactions with medications?
Major
Warfarin (Coumadin) is used to slow blood clotting. There are several reports showing that taking glucosamine sulfate with or without chondroitin increases the effect of warfarin (Coumadin), making blood clotting even slower. This can cause bruising and bleeding that can be serious. Don't take glucosamine sulfate if you are taking warfarin (Coumadin). Many natural medicines can interact with warfarin (Coumadin).
Moderate
Some of these medications are etoposide (VP16, VePesid), teniposide (VM26), and doxorubicin (Adriamycin).
Minor
Some medications used for diabetes include glimepiride (Amaryl), glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase PresTab, Micronase), insulin, pioglitazone (Actos), rosiglitazone (Avandia), chlorpropamide (Diabinese), glipizide (Glucotrol), tolbutamide (Orinase), and others.
Are there interactions with herbs and supplements?
There are no known interactions with herbs and supplements.
Are there interactions with foods?
There are no known interactions with foods.
What dose is used?
The following doses have been studied in scientific research:
BY MOUTH:
- Osteoarthritis: 1500 mg once daily or 500 mg three times daily.